When I launched my School Leadership Mastermind for school principals and administrators back in June, I wasn’t quite sure what to expect. It was my first time running a mastermind group of any kind and, while I had participated in and gained from other masterminds, running my own would be a totally different experience. Particularly in the throes of a COVID pandemic that had put school leaders back on their heels for months.
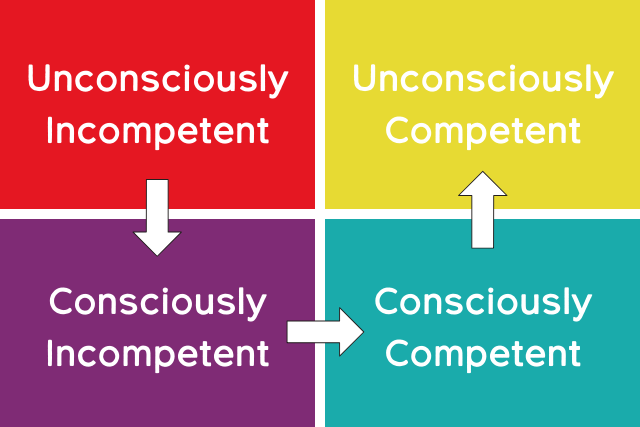
Read MoreWe all want our people to do good, competent work. We also want them to work quickly, without having to think extensively each time about what it is that they’re doing. In other words, we want them to develop to a level of unconscious competence.
Researchers have identified four stages that people progress through as they develop their skills in various areas. Initially (stage 1,) individuals are unaware of how little they know about their knowledge or skill deficits. They are unconscious of the scope of their incompetence and are consequently unlikely to take meaningful action to increase their capacity.
Read MoreFinding the right person to delegate to may not be enough. Often, that person – experienced or not – is going to need to learn new concepts and skills to do their job correctly and efficiently.
One of the first questions you want to ask is, “what do you need to learn in order to do this task properly?” Once s/he has responded, add whatever you feel may still be missing. At that point, work to determine how s/he is going to get the needed training.
Read MoreFollowing are more tips to help keep feedback conversations constructive.
Be growth oriented – The primary purpose of feedback should not be assessment. Rather, it should be on coaching employees to grow and set new goals. Once goals are set, use them as a baseline for future conversations with a focus on how the employee is progressing towards his/her goals. If insufficient progress is being made, use the conversation to figure out why and what can be done to help get things on track.
Be reasonable – Even if there are many correctable items that you’d like to discuss, avoid overloading. Too much information will only dilute the conversation and reduce its effectiveness. Choose the 2-3 most important elements that require attention and leave all others alone. Less is more.
The following list of suggested strategies are rules that we followed that I believe can help you deliver the kind of useful and meaningful PD to your teachers that they need and deserve.
- Develop a 3-5 year plan. Before you do anything else, you need to know what your PD and growth-related goals are, for the short and medium range. Too often, principals live in the moment and make decisions on what feels right. Worse, they may feel obligated to offer “something” simply because it’s on the calendar. The risks in doing so, however, is that you can fail to deliver what is really needed. By developing a 3-5 year plan of the PD areas that you would like to focus on for your staff, you can approach the topic strategically and start to figure out such important areas as topics, schedule, budget and more. You can also loop back from time to time to reinforce and deepen previous learning, especially now that there’s been meaningful opportunity for them to practice.
- Revisit the plan annually (if not sooner). We all know how quickly the winds could blow in the field of education. Yesterday’s “hot” topic can easily be replaced by tomorrow’s latest and greatest. By revisiting your list often, you can start current and see how such changes may or may not impact your thinking.
- State and repeat: “One size fits none.” As with classroom instruction, PD also needs to be differentiated. We cannot expect our middle-school language teachers and our primary-grade teachers to benefit equally from the same presentation. Yes, some topics are generic and can be presented to an entire staff. However, there needs to be various examples for different sub-segments of the population to relate to. More about this later.